Researchers Propose Novel Method to Detect Individual Populus euphratica Tree in Sparse Desert Forests
2024-05-21
In a study published in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, a research team led by Prof. LI Junli from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography (XIEG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have provided an effective method to detect individual Populus euphratica tree in sparse desert forests.
Populus euphratica is vital for environmental protection in arid regions due to its ability to prevent soil erosion, conserve water, and maintain biodiversity. Mapping individual Populus euphratica trees using remote sensing imagery is crucial for monitoring their health and distribution, enabling effective conservation strategies and sustainable management of these critical ecosystems.
However, detecting individual Populus euphratica trees is a challenging task due to overlapping habitats with Tamarix chinensis, as well as the overlapping crowns in clustered Populus euphratica .
To address these challenges, the researchers developed a comprehensive method for accurate detection. First, a deep learning-based semantic segmentation model was employed to distinguish between Populus euphratica and Tamarix chinensis. Then, a constrained two-dimensional bin packing model was used to detect individual trees in clustered Populus euphratica.
In this model, clusters of Populus euphratica trees are treated as containers with spatial and spectral constraints, while individual tree crowns of varying sizes are considered as items for filling the container. Based on a greedy "bigger-first" principle and spatial-spectral constrained search strategy, a heuristic algorithem was designed to obtain the maximum number of individual trees within each cluster.
The researchers successfully detected 22,296 individual Populus euphratica trees in a WorldView-2 image capturing sparse desert forests in the lower reaches of the Tarim River. They also compared the proposed method with traditional detection methods and demonstrated its superiority for detecting individual trees in high-density overlapping clusters.
This study provides an effective solution for similar tasks related to individual tree detection in natural forests, which is of great significance for environmental monitoring, conservation planning, and sustainable ecosystem management.
Article link:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10505319
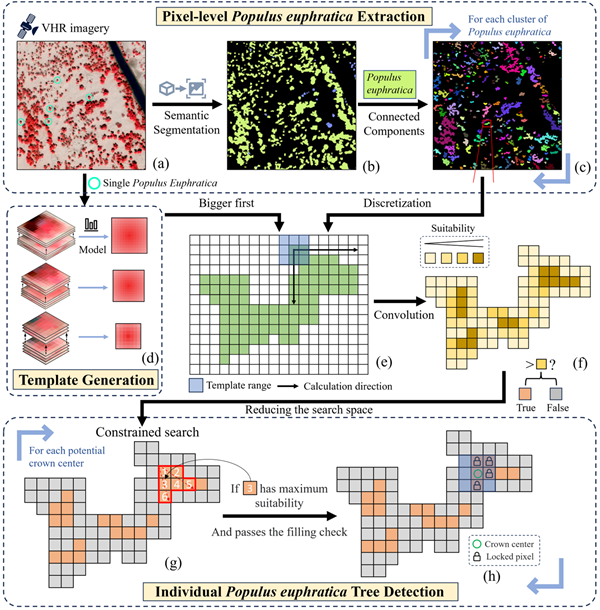
Illustration of the proposed individual tree detection method. (Image by XIEG)
Contact
LONG Huaping
Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography
E-mail: longhp@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Web: http://english.egi.cas.cn



