Study Reveals Effects of Multiple Global Change Factors on Litter Decomposition Rate
2024-05-29
Litter decomposition is a crucial nutrient cycling process in terrestrial ecosystems. However, it may undergo significant alteration under global changes, including nitrogen and phosphorus deposition, warming, drought, and increased precipitation.
In a study published in Soil Biology and Biochemistry, researchers led by Prof. ZENG Fanjiang from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography (XIEG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences elucidated the responses of litter decomposition rate (k) to multiple global change factors (GCFs).
Researchers conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis by constructing a dataset based on 260 papers and 1706 observations, which were collected from the Web of Science and China National Knowledge Infrastructure.
They found that nitrogen addition and drought had significant negative effects on k; phosphorus addition, warming, and increased precipitation had positive effects on k; elevated CO2 had an insignificant effect on k. They also found the combined effects of multiple GCFs on k can offset each other.
Besides, the researchers found initial litter quality, soil properties, environmental factors, and experimental methodology significantly influenced the effects of nitrogen addition, phosphorus addition, warming, drought, and increased precipitation on k.
This study provides new insights into how global change affects litter decomposition, and more work is needed for accurate predication.
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2024.109474
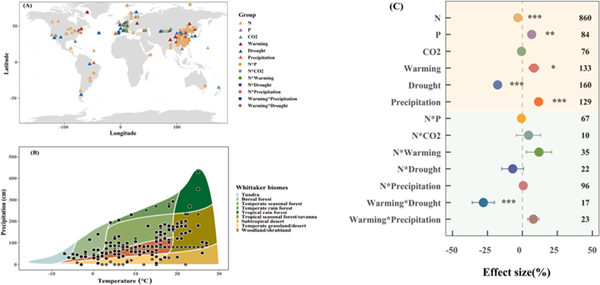
Geography (A) and climate distribution (B) of meta-analysis observations, and effects of global change factors on k (C). (Image by XIEG)
Contact
LONG Huaping
Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography
E-mail: longhp@ms.xjb.ac.cn



