Critical Snowfall-to-Precipitation Ratios Identified in High Mountain Asia Amid Global Warming
2025-02-25
A recent study, published in npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, has identified critical thresholds of snowfall-to-precipitation (S/P) ratios sensitive to global warming, as well as their projected future trajectories in High Mountain Asia (HMA).
Using ERA5-Land historical climate data and Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) model projections, researchers led by led by Prof. CHEN Yaning from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography (XIEG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences applied piecewise linear regression analysis to differentiate the impacts of rising temperatures from precipitation phase (e.g., rain or snow) changes. This allowed them to identify nonlinear thresholds in the S/P ratio.
The researchers identified two pivotal S/P ratio thresholds—0.13 and 0.87—and classified HMA into four distinct regions: insensitive snow-dominated areas (S/P > 0.87), sensitive snow-dominated areas (0.5<S/P <0.87), sensitive rain-dominated areas (0.13<S/P <0.5), and insensitive rain-dominated areas ((S/P<0.13).
They found that snow-rain transition areas (0.13 <S/P<0.87) showed heightened sensitivity to global warming, with snowfall rates declining 3 to 5 times faster than those in snow-dominant areas (S/P > 0.87) or rain-dominant areas (S/P < 0.13). This nonlinear response challenges assumptions of uniform snowfall reductions under warming conditions and highlights the disproportionate vulnerability of transitional areas.
Furthermore, the researchers projected future precipitation patterns under the Shared Socio-economic Pathway (SSP5-8.5) scenario, revealing that global warming is likely to cause all the four regions to migrate to higher elevations. Snow-dominated areas are expected to shrink by 25.8% in winter and 54.1% in spring by 2100, while rain-dominant areas are anticipated to expand, covering over 80% of HMA during the summer and autumn. These changes are primarily driven by rising temperature rather than shifts in precipitation patterns, significantly affecting water storage and ecosystem stability in the region.
"We provide a framework to identify snow-rain thresholds,” said Dr. LI Yupeng, first author of the study. “This is essential for predicting water resource availability in Asia's mountain systems, where snowmelt supports rivers that provide water for billions of people downstream.”
The study lays a groundwork for climate adaptation strategies, urging closer monitoring of regions that exceed critical thresholds to better understand and mange the impacts of global warming on water resources in the region.
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-025-00935-y
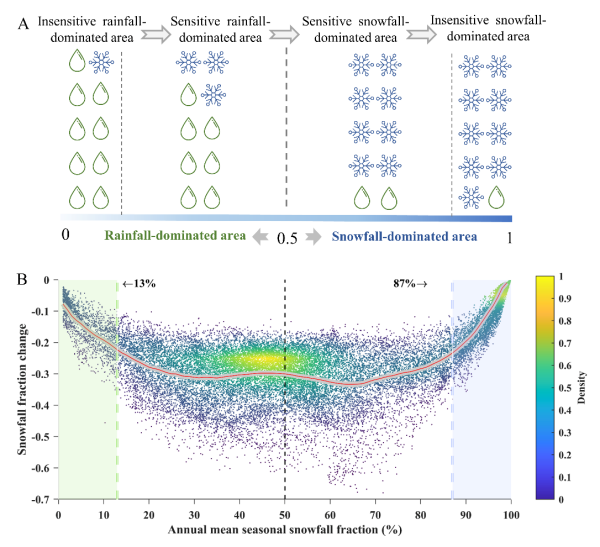
Identification of critical snowfall-to-precipitation thresholds (Image by XIEG)
Contact
LONG Huaping
Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography
E-mail: longhp@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Web: http://english.egi.cas.cn



